General Information
INDUSTRY STANDARDS AND SPECIFICATIONS
The Manufacturers Standardization Society (MSS) has standard practices SP-58 and SP-69 which are widely used in our industry. ASME B31.1 and B31.3 are important standards for piping in the power and petrochemical industries. Moreover, many of our customers have their own standards and designs for pipe supports. At Piping Technology & Products, Inc., we always keep these guidelines in mind and manufacture your supports to their strict specifications. In this section, you will find our standard variable and constant pipe supports.
TYPES OF VARIABLE SUPPORTS
The term “type” is used with an alphabetical designation (A-G) to describe seven different physical connections to the supporting structure. The figure below illustrates the applications and the physical connections for each type. Hangers are suspended from structural members while base supports (Type F) rest on a supporting surface.
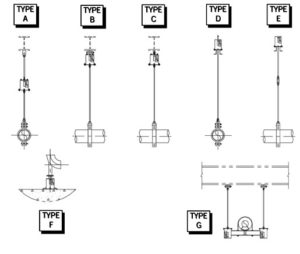
Type A: The spring support is furnished with a threaded bushing in the top plate, providing for a simple rod attachment for the upper connection.
Type B & C: The spring supports are furnished with one or two lugs welded to the top cap plates of the casing.
Type D: The spring support permits adjustment from the top, by turning the nuts on the hanger rod against a piece of tubing. The tubing is securely welded to the spring cap. In type D, the spring is set above the supporting steel.
Type E: The spring support permits rod adjustment from either above or below the spring. The type E spring is set above the supporting steel or can be welded directly to the supporting steel from below.
Type F: The spring support is designed to support piping from below, directly from the floor or supporting steel. Adjustment is made by inserting a bar into holes in the load column and turning the load column as a jackscrew. The base plate is bolted to the case and has four holes for fastening. The installed height of the base (F-type) spring should be specified as follows:
• With upward movement from cold to hot position: The installed height should be the midpoint between the minimum and maximum “X” dimension plus the thickness of the load flange.
• With downward movement from cold to hot position: The installed height should be the midpoint between the minimum “X” dimension plus the load flange thickness plus the amount of the vertical movement.
Type G: The spring support assembly is formed by welding two standard spring assemblies to the ends of a pair of channels. Type G assembly can accommodate unusually heavy loads and is especially adaptable for avoiding interference in spaces where the headroom is limited. The assembly can be furnished with center-to-center dimensions, as specified by the purchaser. When ordering Type G, divide the total pipe load in half to select the proper spring size. The travel range of the springs remains unchanged.
The way a variable spring support responds to an applied load depends on the coil or coils inside the casing. Each coil arrangement has a spring rate expressed in units of pounds/inch (or kilograms/millimeters) of compression. The required coil size is determined by load while the required number of coils (length) is determined by the anticipated range of movement. A longer coil or coils placed in series will provide greater travel for similar loads. Manufacturers use their figure numbers to designate the coil arrangements which provide greater movement. At Piping Technology & Products, Inc., we use PTP-1, PTP-2, PTP-4, PTP-6, and PTP-8 to designate the five standard coil arrangements we employ to increase the working range of travel of variable supports. The Load and Travel Tables are color-coded to identify the travel and spring rates for each PTP figure number. These tables can be used to select the PTP figure number and size required for a particular application.
PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS
The physical dimensions of variables are different depending on the figure number and size you have selected. The following pages provide drawings and dimensions for every combination of PTP’s standard variable supports. If you have a requirement for which you do not have clearance for the standard spring, please contact us about a modification to satisfy your requirement.
During assembly the coils are pre-compresse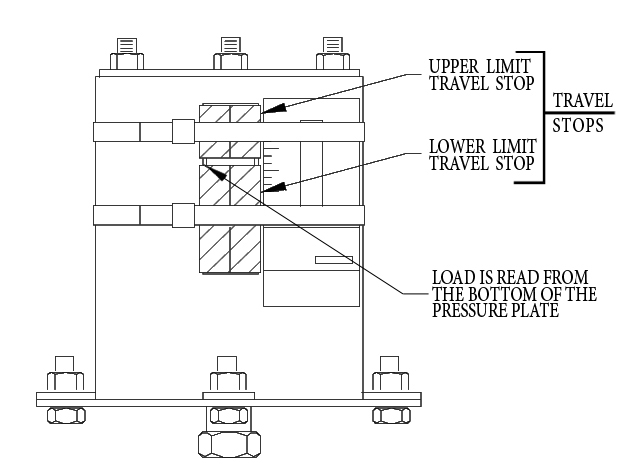 d and travel stops, which are painted red, are installed and banded in place with steel bands as shown in the figure to the right. Any load, such as in hydro-testing of the pipe, applied to the variable spring prior to removing the travel stops will not be applied to the coil. When the installation is complete, the travel stops must be removed so the variable spring can function properly.
d and travel stops, which are painted red, are installed and banded in place with steel bands as shown in the figure to the right. Any load, such as in hydro-testing of the pipe, applied to the variable spring prior to removing the travel stops will not be applied to the coil. When the installation is complete, the travel stops must be removed so the variable spring can function properly.
FINISH
Galvanizing provides the most cost-effective finish for use in corrosive environments. Because the majority of our customers specify galvanized finish, we maintain a large inventory of galvanized components which enables us to assemble and ship variables very quickly. A longer delivery time may be required when finishes other than galvanized are specified.
SPECIAL FEATURES
Special features can be provided with the PT&P standard variables when required. For example, lifting lugs, such as those shown in the figure on the right, can be helpful for installing large hangers. Other special features include upper and lower limit stops, guided load columns, jacking bolts, PTFE 25% glass filled slide plates, collars or extended load columns. Special features may increase the price and the time required for delivery.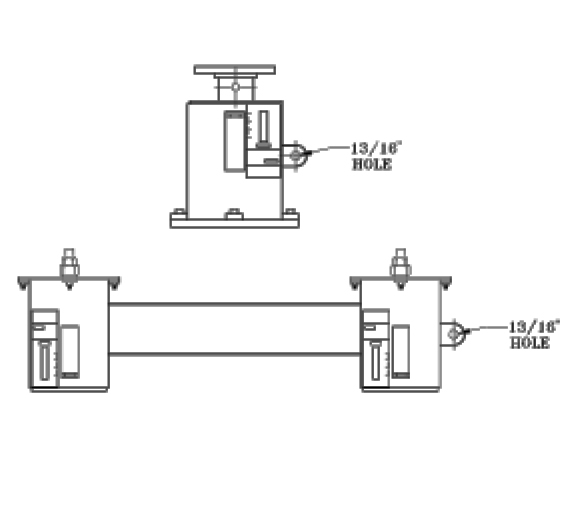
FEATURES
1. Precompression – precompressing the spring coil into the hanger casing saves headroom and erection time.
2. Slots in the casing at two locations 180 degrees apart allowing for complete in-service visual inspection of the spring coil and other internal components.
3. For each series, there is a reserve travel at the upper and lower limits of the working range of the hanger, and any travel beyond this reserve travel becomes either free up movement or a limit stop for downward travel.
4. The allowable stress of the coil spring conforms to MSS SP-58.
5. All-steel construction-spring and casing are fabricated of steel and are rugged and compact.
6. Anti-corrosive material (stainless steel) is used for the nameplate.
7. Load Indicators are clearly visible in the slot and are easily readable.
8. The piston plate serves as a centering device or guide, maintaining spring concentricity under eccentric loads.
9. The finish is hot-dipped galvanized, or other, as specified.
10. All F-type supports are supplied with a load flange.
