Download PDF
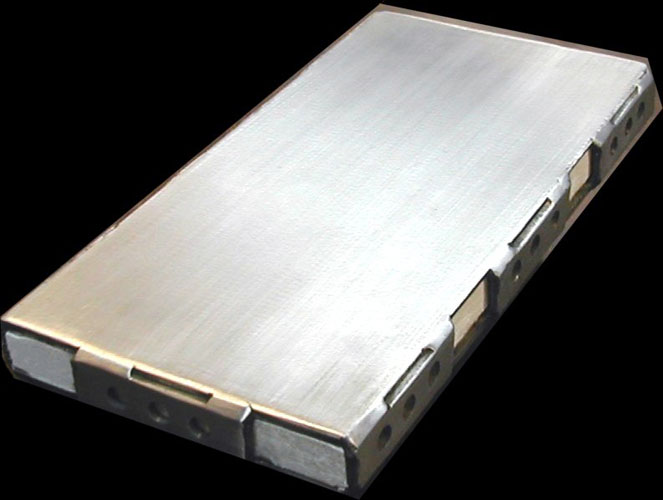
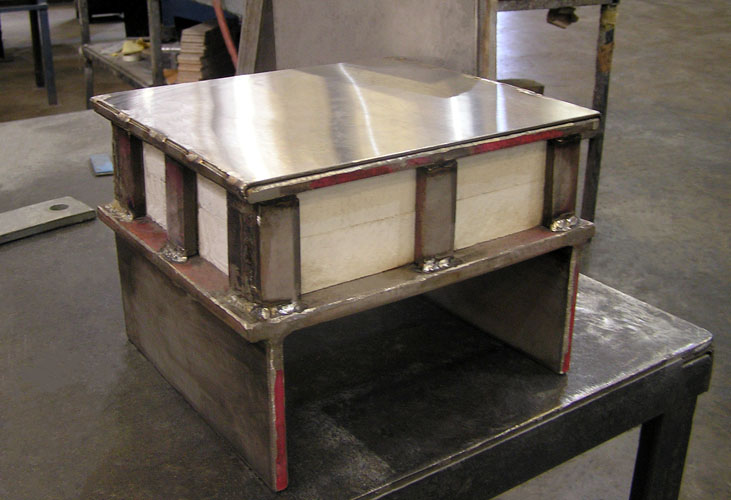
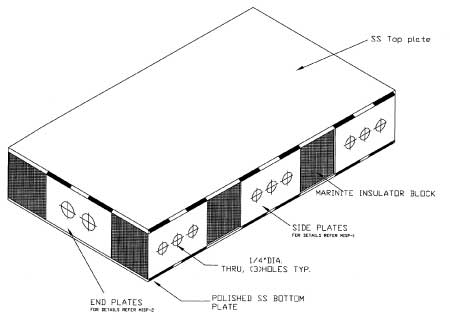
Piping Technology & Product’s marinite slide bearing plates are rectangular slide-plate assemblies consisting of a marinite insulator block sandwiched between stainless steel top and bottom plates. These marinite slide bearing plates are held together by side plates along the length, and end plates along the width of the assembly.
Marinte Plates Construction
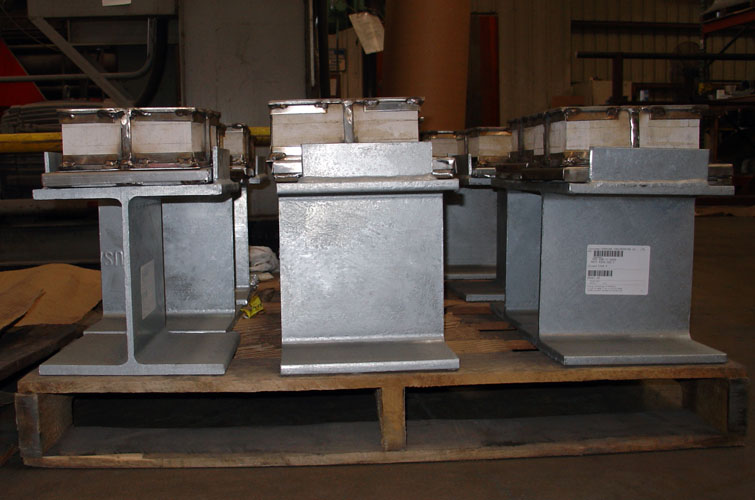
The side and end plates have 1/4″ diameter through holes and are stitch welded to the top and bottom plates. The bottom plate is polished to a mirror finish for sliding along the surface of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) with minimal coefficient of friction. The assembly is generally welded to shoes.
Coefficient of Friction:
0.08 @ minimum pressure
0.06 @ maximum pressure
Marinte Plates Application
The marinite insulator assembly allows the use of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) as the sliding surface for lines with high operating temperatures and high dynamic loading. It protects the polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) by acting as a barrier to heat transfer. It has so far been used for power plants — high energy systems (SHP, SIP). It could potentially be used wherever there are movements at top, bottom or laterally at the point support.
So the benefits of having a marinite insulator include:
• Facilitates use of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) on high-temperature lines.
• Marinite being a high load bearing insulation material is ideal for the dynamic conditions.
Marinite Plates: PT&P’s Capabilities
Piping Technology & Products is a supplier of marinite slide bearing plates, which through proven testing allows for the use of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) as the sliding surface for lines, even under extremely high operating temperatures. Piping Technology & Products has supplied these plates for a number of companies in the oil, gas and power industry.

Marinite can be used as the insulating material in hot piping supports. The most widely known grade for Marinite is grade P. Marinite-P is most often used as structural insulation because of its high dimensional stability. Marinite-P is incombustible, provides high insulation values, and high compressive strengths and is thus appropriate in high-load and high-temperature applications. The material minimizes decay, rust, and corrosion and it resists damage during installation and provides durable service. The material acts as a suitable insulator in fireproofing and heat processing equipment applications up to 1200°F (649°C).
Major Advantages:
• High Compressive Strength.
Deflects less than 1/10 in. per inch of thickness under 4000 psi
Deflects less than 3/64 in. per inch of thickness under 2000 psi
• High Tensile strength.
• High resistance to shear and traverse forces.
Major Applications:
• Hot Line Pipe Supports in Power Generation and Process Industries
• Structural Insulation in Pipe
• Supports Backup Insulation in Rotary Kilns of Lime and Cement Plants.
• Ceramics and Foundry applications.