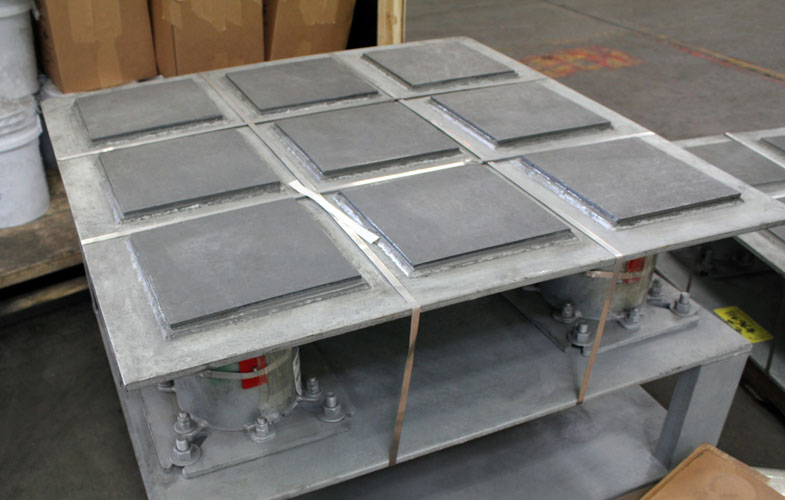
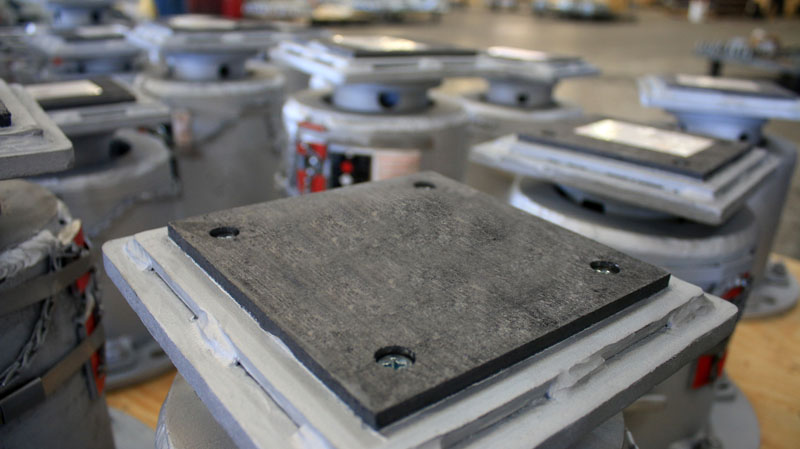
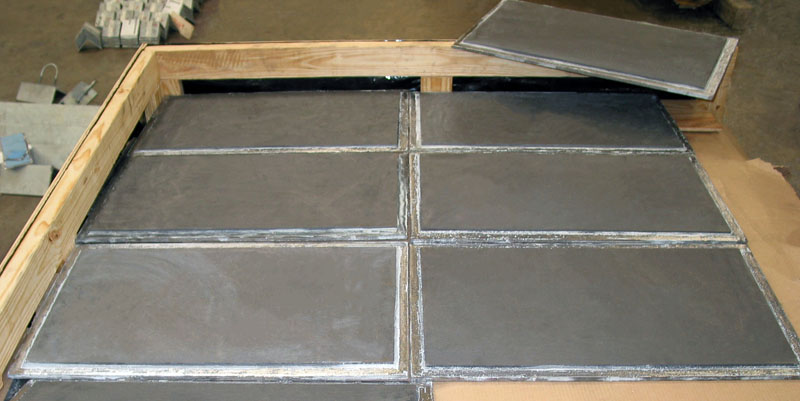
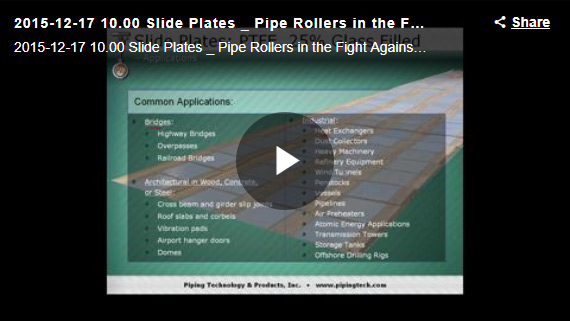
Graphite Slide Plates
Graphite slide plates can be used in place of PTFE, 25% glass filled slide plates for higher temperature applications. Pure Graphite Slide Plates are recommended for those systems which produce exceptional pressure and heat. With a range of up to 1,000 degrees Fahrenheit for ambient conditions and 3,000 degrees Fahrenheit for inert settings, graphite slide plates can also handle up to 2000 PSI.
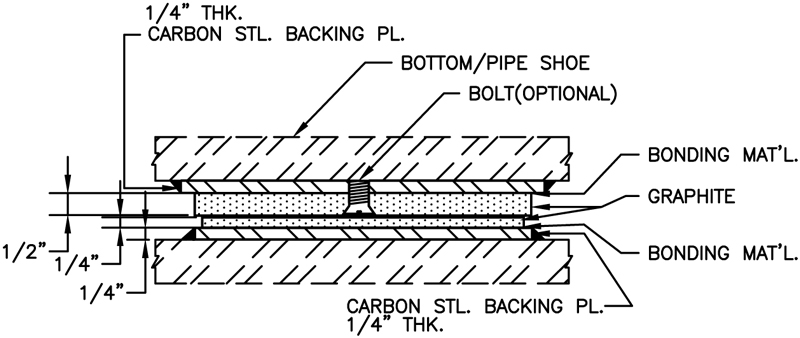
Graphite Slide Plates Diagram

Download Graphite Slide Plate General PDF
The graphite plates come in two different configurations, the ‘bonded’ and ‘bolted’ assembly. The bonded configuration consists of a ¼” thick graphite pad bonded to a metal backing plate. The bolted configuration consists of a ½” thick graphite pad bonded and bolted to a metallic backing pad. Both configurations can either be tack welded or fully welded to support components.
ASSEMBLY:
Standard Assembly: 2 units of Graphite bonded to 1/4″ carbon steel. For field tack welding. 1/4″ lip. Loads to 2000 PSI, Temperature: +1000° F air, +3,000° inert
Full Weld Assembly: 2 units of Graphite bonded to indicated backing material with 1/2″ lip all around for full welding. Load to 2000 PSI, Temperature: +1000° F air, +3000° F inert
PART # — PTP — Graphite (1/2″ or 1/4″) — 10 Ga. SS — 1/4″ LIP AND SIZE
ADVANTAGES:
- High operating temperature.
- Ease of installation.
- No setting problems.
- Low coefficient of friction.
- No surface treatments, grouting, or expensive mechanical attachment necessary.
- Chemically inert.
- Unaffected by weather conditions.
- Ability to absorb dirt and grit within itself.
- Self-aligning when used in conjunction with elastomeric backing pads.
ORDERING:
- Please specify the dimensions of the upper plate and dimensions of the lower plate. It is common practice that the upper plate is generally larger than the lower plate.
- Specify lip dimension (if different than the standard 1/2″).
- Specify base plate thickness (if different than standard 1/4″).
- Bolting upper plate is recommended at temperatures above 200°F.
APPLICATIONS:
- Bridges: Highway bridges, overpasses, railroad bridges.
- Architectural in Wood, Concrete or Steel: Cross beam and girder slip joints, roof slabs and cor-bels, vibration pads, airport hangar doors, domes.
- Industrial: Heat exchangers, dust collectors, heavy machinery, refinery equipment, wind tunnels, penstocks, vessels, pipelines, air preheaters, atomic energy applications, transmission towers, storage tanks, offshore drilling rigs.
| Property (Room Temperature) | Units | Average | Units (metric) | Average |
| Bulk Density | lbs./ft.3 | 99.26 | Mg/m3 | 1.59 |
| Specific Resistance With Grain Across Grain | 10-4 ohm-in. | 3.33 4.74 | ohm-meter | 8.47 12.05 |
| Flexural Strength With Grain Across Grain | PSI | 1297 995 | kPa (kN/m2 ) | 8940 6860 |
| Tensile Strength With Grain Across Grain | PSI | 713 630 | kPa (kN/m2) | 4920 4340 |
| Young's Modulus With Grain Across Grain | 106 PSI | 0.96 0.61 | MPa (MN/m2) | 19840 19320 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion With Grain Across Grain | 10-6 / °F | 0.72 1.35 | 10-6 / °C | 1.32 2.43 |
| Thermal Conductivity With Grain Across Grain | BTU x ft. hr. x ft.2 x °F | 88 62 | W/m x °C | 152 107 |
| Permeability With Grain Across Grain | Darcy's | 0.493 0.444 |
||
| Coefficient of Friction | 0.15 | 0.15 |